The 2025 M&A Outlook indicates a steady recovery in dealmaking owing to a stabilizing macroeconomic environment and the reopening of financial markets.
Financial due diligence in business transactions like M&As implies an accurate valuation to provide insights into the target company’s market value.
The buy side performs financial due diligence on a target company by examining its financial standing, including statements, physical assets, and revenue streams. The process is critical to ensuring that the stock purchase price of a target company corresponds with its worth.
The financial due diligence process explores a target company’s financial performance to detect hidden risks and forecast growth prospects.
Inadequate financial due diligence may lead to:
- Legal consequences
- Fines and litigation
- Disruption of business operations
- Failure to meet contractual obligations and the terms of other agreements
- Reputational losses
- Regulatory non-compliance
- Costly investigations
- Brand devaluation.
Today’s blog post provides a comprehensive due diligence checklist, including best practices for conducting financial due diligence, leveraging virtual data rooms, and the red flags to avoid in financial due diligence.
What is Financial Due Diligence?
Financial due diligence assesses the target company’s financial performance to identify potential risks and forecast its future.
Financial due diligence is a broader term than financial audit. A financial audit verifies whether income statements, recent balance sheets, and cash flow reports are accurate.
The financial due diligence report examines the numbers to determine whether the provided figures are sustainable and to uncover any hidden liabilities. This allows the buy side to grasp the target company’s key performance metrics. It also helps the buy side to assess whether the past performance complies with the company’s future potential.
As a thorough audit of the financial information provided by the sell side, financial due diligence verifies whether the potential deal holds a decent perspective.
The financial due diligence team confirms financial information critical for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) deals and investment processes.
To assess the target company’s cash management, financial stability, liquidity, and profitability, the financial due diligence process embraces:
- Balance sheet examination
- Cash flow insights
- Income statement analysis.
Best data rooms for due diligence
Overall rating:
4.9/5
Excellent

Overall rating:
4.8/5
Excellent
Overall rating:
4.7/5
Excellent
Financial Due Diligence Checklist: Key Components
This section is pivotal as it presents the detailed checklist of the target company’s key information reviewed during financial due diligence:
- Asset turnover
- Balance sheets, including assets and liabilities, over the past five years
- Cash flow statements, including cash inflows and outflows over the past five years
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Financial meetings, including meeting minutes
- Income statements, including income and expenditures over the past five years
- Interest coverage
- Gross margin
- Operating margin, except for taxes and interest charges
- Profit margin
- Return on assets
- Return on equity
- Tax due diligence
| Financial statement analysis Due diligence analysis of the target company’s financial statements assumes substantial benefits: Performance evaluation Risk mitigation Investor confidence Regulatory filings and legal compliance Informed decision-making. | To gauge the target company’s financial health, financial statement analysis examines: Assets Balance sheet Cash flow statement Earnings and revenue Expenditures and expenses Financial standing Income statement Gross profit margin Liabilities Liquidity and solvency Net assets Net profit margin Operating profit margin. |
| Revenue and profitability trends To calculate revenue projection, it is vital to multiply the target company’s projected sales by the expected, considering growth rates, market demand and sales volume fluctuations. | To calculate revenue growth as a percentage, you should subtract the previous revenue from the current period’s revenue and divide it by the target company’s historical revenue. |
| Liabilities and Debt Structure Financial obligations include outstanding debts or regular payments incurred by the target company. | To assess outstanding debts and obligations, financial due diligence helps to divide the target company’s total monthly debt by its gross monthly income. The target company’s monthly loan payments should be multiplied by twelve to determine an annual debt obligation. The annual earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) should be divided by the target’s annual debt requirements. Whenever the debt-to-income ratio exceeds 43 percent, the target company is bound to run into debt. |
| Tax compliance A tax compliance report indicates whether the target company has duly filed tax returns and met its tax obligations. | Financial due diligence helps to verify the target company’s tax filings and potential liabilities. The target company should determine its taxable income by calculating total revenue, except for deductions and exemptions. |
| Operational costs Operational costs consist of fixed and variable expenses: – A ‘fixed expense’ is a set amount of costs with an intact price and frequency. – A ‘variable expense’ changes depending on how many units the target company sells. | Financial due diligence helps to calculate the target company’s operational cost by aligning day-to-day business expenses and all operating expenses like rent, wages, salaries, operational utilities, and marketing costs. |
| Legal and regulatory compliance Financial due diligence ensures the target company’s adherence to financial regulations to safeguard the target company’s compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. | Financial due diligence comprehensively reviews the target company’s legal contracts and obligations and detects all possible legal issues, like non-compliance areas and potential liabilities. |
| Risk assessment Financial due diligence helps to identify the target company’s financial risks that can adversely affect its business stability. | Core risk factors affecting the target company’s competitiveness vary from costs and inventory to market fluctuations and government regulations. |
Best Practices for Conducting Financial Due Diligence
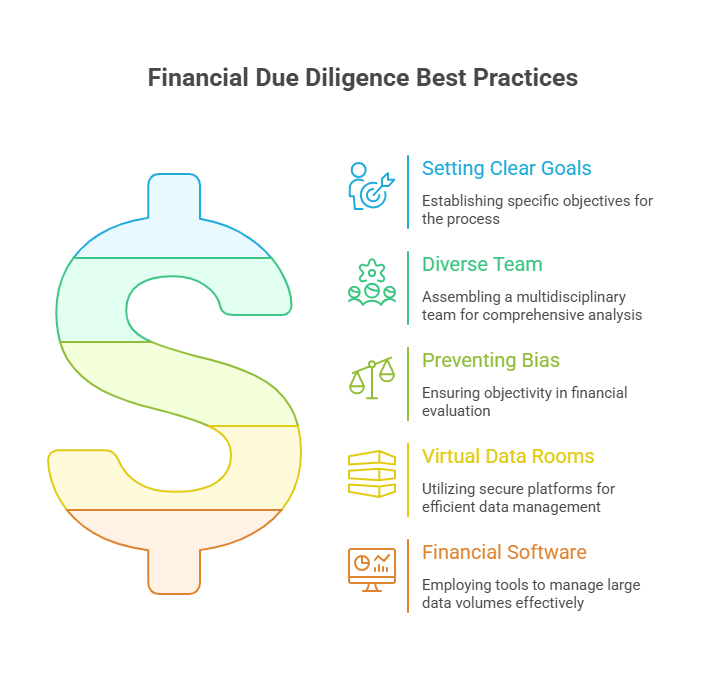
The best financial due diligence practices entail:
- Setting clear goals and objectives
- Arranging a diverse, multidisciplinary financial due diligence team
- Preventing confirmation bias to ensure an objective financial evaluation
- Leveraging virtual data rooms to make the financial due diligence process complete and efficient
- Utilizing financial due diligence software to manage large volumes of data
Systematic approach to financial due diligence
Developing a systematic approach to financial due diligence review is a core prerequisite, ensuring a successful outcome for the buy side and the sell side of a business transaction.
As a key process in M&A, financial due diligence takes place before a deal to ensure a thorough comprehension of the target company’s financial standing.
The financial due diligence process appraises the target company’s historical and current state and the accuracy of its financial information. On this decent background, the buy-side M&A or potential investors get informed about the core metrics of the target company’s financial performance.
Key documents needed for the financial due diligence:
- Assets and liabilities
- Audited financial statements
- Balance sheets
- Cash flows
- Capital expenditures
- Projections
After submitting a letter of intent and confidentiality agreement by the M&A buy side, the M&A sell side should arrange all the financial data to support the claims following initial conversations.
As an outcome, the financial due diligence aims to reveal the target company’s fair market value.
Proper comprehension of the target’s financial health will help to ensure a sound investment. The major value of financial due diligence for the buy side financial performance is to raise the buyer’s confidence in an M&A deal.
Common mistakes to avoid
Downplaying financial due diligence causes poor business deal decisions, financial losses, and underestimation of the target company’s real value:
- Neglecting preliminary due diligence assessments
- Failing to review the target company initially
- Providing an inadequate financial analysis of the target company will result in its overvaluation
- Neglecting legal liabilities will result in financial penalties, reputational losses, and unexpected legal issues post-acquisition target
- Overlooking operational efficiencies will harm the target company’s profitability and competition potential.
Importance of independent verification and third-party audits
Financial due diligence deploys independent (impartial) verification and validation assessments to spot any inconsistencies related to the target company.
As part of financial due diligence, verification confirms the target business entity’s declaration of tax returns and retained earnings.
Tax returns are under scrutiny in audit investigations during financial due diligence
Third-party audits entail independent evaluations by external organizations to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the target company’s compliance with applied industry trends and standards like ISO 9001 and relevant regulations.
The independent auditors assess the target company’s financial statements. The verification process examines liens, charges against assets, liabilities, and the legal ownership of other valuable assets.
Using Virtual Data Rooms for Financial Due Diligence
Benefits of using a virtual data room (VDR) for document management
Proceeding with financial statements, market forecasts, and industry data assumes coping with the sensitive information. While M&A sellers and buyers share confidential and other organizational documents, they deploy secure deal rooms.
Virtual data rooms (VDRs) help parties and key stakeholders streamline due diligence success in business and investment transactions by providing secure sharing, document indexing, and audit trails.
The parties conduct financial due diligence to check the validity of legal transactions and audit all the related documentation. For this essential purpose, a virtual data room is a secure online environment to safeguard a thorough review of confidential information.
VDRs are secure storage and distribution hubs applicable to all relevant documents and files processed during due diligence.
Virtual data rooms are secure online repositories integral to financial due diligence. Set as a folder-and-file structure, they help set up folders for finance, legal, human resources, tax, real property taxes, stock purchase agreements, and intellectual property files.
How VDRs streamline financial due diligence
Financial due diligence is mostly about a comprehensive understanding of the seller’s performance in the corporate finance context to provide the buyers with well-informed strategic decision-making:
- Is the buyer acquiring a financially sound company?
- Are there considerable flaws in the target company’s business model enough for the buyer to pull out of the deal?
- Are the red flags associated with the company’s financials, like non-compliant accounting policies with industry standards?
- Does the target’s financial condition fit the buyer’s expectations?
The cases showing how VDRs streamline financial due diligence:
- End-to-end encryption to safeguard shared data
- Document organization
- Due diligence checklists
- Dynamic watermarks to disable unauthorized use
- Granular permissions for individual user roles
- Multi-factor authentication
- NDA integration
- No unauthorized document downloads
- Q&A modules
- Real-time activity tracking
- Time-limited document access
- Tracking user activities with audit trails
- Setting access permissions.
Best VDR providers for financial due diligence
Our top virtual data room providers secure the confidentiality of:
- Audits
- Financial statements
- Tax returns
- Tax liabilities
Clear document organization enables file arrangement and grouping by folder names like legal, financial, or operational.
| VDR Provider | Description |
| Ideals | The internationally acknowledged virtual data room provider renders top-level financial, operational, and commercial VDR support for all types of businesses. The repository provides a virtual filing cabinet with automatic indexing to store balance sheets, profit and loss statements (P&L), financial statements, records, employment contracts, and other sensitive data integral to the financial due diligence process. Advanced tracking tools and password protection ensure confidentiality and agile data management. Fence view, redaction, and watermarking are time-tested data security features. Ideals is compliant with the US industry standards like FINRA. |
| SecureDocs | The top vendor features efficiency, security,, and remote functionality. SecureDocs provides solid data room solutions for sensitive data protection and specialized permissions for financial due diligence teams. SecureDocs simplifies financial due diligence by user monitoring, access restrictions, and convenient document sharing options. |
| DFIN | The intuitive virtual data room platform features utmost security optimization. Businesses leverage the productivity and usability of the financial due diligence process. |
Common Red Flags in Financial Due Diligence
In the course of financial due diligence, executive teams dive deep into the target’s financials. Mostly, they are detecting the red flags like:
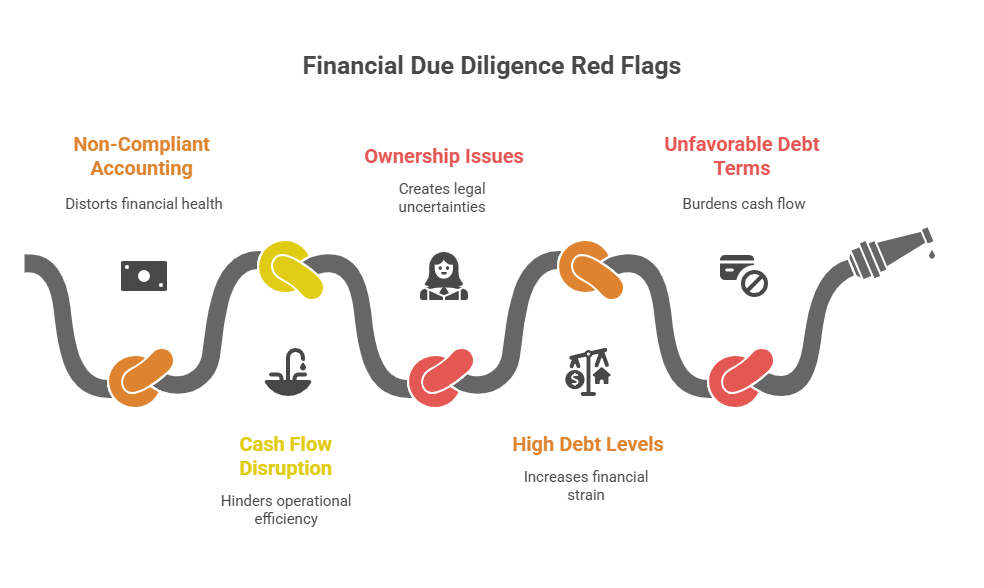
- Non-compliant accounting practices with industry standards
- The target’s cash flow disruptions
- Ownership issues related to contentious assets
- Current debt levels
- Interest rates and terms involving indebtedness
- Violation of money laundering regulations
- The target’s profit margins eroded due to market competition or higher expenses
- The target’s fixed and variable costs
The warning signs that signal the buy side investors about the target’s potential financial risks include, though are not limited to:
Inconsistent financial statements involve discrepancies in financial records, indicating inconsistencies in the target’s financial data due to human errors in data entry, record-keeping failures, or fraudulent activities.
A high debt-to-equity ratio, typically above 2, signals to investors about risky investment opportunity while the target company will not earn enough to repay its debts. Once the target’s debt ratio is closer to zero, it means that the target did not borrow external funds to support its operations.
Unusual revenue spikes or declines without a clear reason signal the buy side about the target’s financial irregularities or fraudulent activities. A considerable revenue increase from a particular customer or geolocation signals revenue manipulation or channel stuffing.
Lack of proper financial documentation assumes insufficient documentation provided by the sell side results in legal risks, cost overruns, delays, communication breakdowns, and reputational damages.
Pending legal disputes affecting financials involve costs and risks associated with the enforcement of court claims. Legal disputes have a lasting adverse effect on the target company’s financial performance, considering litigation costs and proceeds.. Pending legal disputes involving the costs paid by the company for legal proceedings reduce the target’s profits and negatively impact the EBITDA outcomes.
Conclusion
A structured approach to financial due diligence is beyond the success of business transactions. The initial check of the target company’s financial documentation often predetermines the course of the deal.
Our article emphasizes the importance of robust financial due diligence in diverse contexts of the target company’s current and potential market standing, including the revision of the target’s assets and liabilities and its commercial potential.
We paid special attention to leveraging the functionalities of virtual data rooms (VDRs) as secure financial data-sharing environments for efficient business transactions.
Our recommended VDR repositories enable business counterparts to objectively appraise the target company’s true value by secure examination of its financial statements, asset purchase quality, and revenue streams.

