Key features:
- Project setup in less than 15 minutes
- Storage-based pricing for clear project budgeting
- In-app live chat support 24/7, including holidays and weekends

Overall rating:
4.8/5
Excellent
Securedocs
Free trial: 14 days
Key features:
- Built-in electronic signatures and templates
- Granular user permissions and activity logs
- Q&A workflows with Excel export

Overall rating:
4.5/5
Good
Onehub
Free trial: 30 days
Key features:
- FTP getaway for mass uploads
- Document previews supporting popular file formats
- Comments and tasks for collaboration

Overall rating:
4.4/5
Good
HighQ
Free trial: Yes
Key features:
- Q&A workflows for bidder interaction
- Custom data room audits
- Custom user invitation letters
Overall rating:
4.7/5
Excellent
DFIN
Free trial: 14 days
Key features:
- AI contract analysis for due diligence
- Automatic PII redaction in uploaded documents
- Multi-deal management and project reporting
In 2024, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, a 10% increase from the previous year and the highest ever recorded, according to IBM. This highlights how important secure data storage has become.
As cyberattacks continue to rise, businesses are increasingly looking for reliable ways to protect sensitive information. In response, virtual data rooms (VDRs) were created to provide a secure solution for high-risk transactions. But how are they different from other file sharing services like Google Drive or Dropbox?
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between cloud storage solutions, helping you determine which is best for securing sensitive data.
Understanding virtual data rooms
A virtual data room (VDR) is a secure online platform used for storing and sharing sensitive documents, typically in high-stakes transactions. VDRs offer advanced security features such as data encryption, watermarks, and granular access controls to protect confidential information.
VDRs are widely used in cases where secure data sharing is essential. For example:
- Mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Companies use VDRs for due diligence, enabling buyers to review financial statements, contracts, and other essential documents securely.
- Legal sector. Law firms store case files, contracts, and confidential client information while ensuring regulatory compliance and security.
- Financial institutions. Banks and investment firms use VDRs for audits, fundraising, and secure file sharing during transactions.
- Real estate. Developers and investors use VDRs to share property-related documents, contracts, and financial records with potential buyers or partners.
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals. Organizations use VDRs to securely store patient records, clinical trial data, and intellectual property.
- Private equity and venture capital. Firms use VDRs to evaluate investment opportunities and securely exchange financial reports with stakeholders.
What is file sharing?
File sharing solutions enable users to securely store, access, and share digital files over the internet. These range from traditional methods like email attachments and FTP (file transfer protocol) to modern cloud-based platforms such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive.
While traditional methods are commonly used, cloud storage services provide more secure and efficient ways to manage and share data, especially for businesses with advanced needs.
Cloud-based solutions are user-friendly, cost-effective, and widely adopted, allowing teams to collaborate in real time from different locations. They simplify file management and reduce the learning curve for users, making them ideal for both personal and business use.
Common modes of file sharing are:
- File transfer protocol (FTP). Transfers files between systems within a network.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. Enables direct file sharing between users.
- Removable storage media. Uses physical devices like USB drives to transfer files.
- Online file sharing platforms. Cloud platforms like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive for remote file storage and sharing.
Key differences between data rooms and different file sharing solutions
Here’s a comparison of data rooms and file-sharing solutions to highlight their key features and advantages.
| Features | Virtual data rooms | File sharing solutions |
| Purpose | Secure document sharing for sensitive information, often in mergers, acquisitions, or legal processes. | General document sharing for everyday use. |
| Data security | Enhanced security features, like high-level encryption, multi-factor authentication, and strict user access control for sensitive documents. | Basic encryption and limited security features, often lacking advanced protections like encryption at rest. |
| User management and permissions | Granular control over who can view, edit, or download files, allowing precise access management. | Simple user access controls, typically offering broader permissions without detailed restrictions. |
| File management | Powerful tools for organizing, categorizing, and indexing files, making it easy to manage large volumes of documents. | Simple file organization with fewer tools for managing a large number of files efficiently. |
| Collaboration | Secure collaboration tools with features like commenting, shared workspaces, and Q&A functionalities. | Basic collaboration tools that may not offer the same level of security or real-time collaboration. |
| Audit trails and reporting | Comprehensive audit trails to track who accessed files, what actions were taken, and when. | Limited or no audit trail features, lacking detailed user activity tracking. |
| Compliance features | Complies with industry standards like GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA. | Compliance varies, may not meet strict standards for sensitive data. |
| Storage capacity | Large storage space options tailored for handling extensive data securely, often with customizable tiers. | Varies widely in capacity, usually offering less storage and fewer customization options. |
| Customization | Custom branding and interface options for a tailored experience. | Limited customization, mainly for basic branding. |
| Integration | Integrates with CRMs, legal, and project management tools. | Integrates with common productivity tools like Google Drive and Dropbox. |
| Additional features | Some data rooms include AI-powered tools and other features to enhance security and document management. | Few additional features beyond basic sharing and storage capabilities. |
| Scalability | Designed for large-scale, complex data-sharing needs. | Best for personal or small business use, not suited for large transactions. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized security and features. | Typically lower cost or free for basic use. |
Therefore, if your business requires advanced security and compliance, secure data rooms are the best choice, but for simple file sharing, basic solutions might suffice.
When should you choose a data room over file sharing?
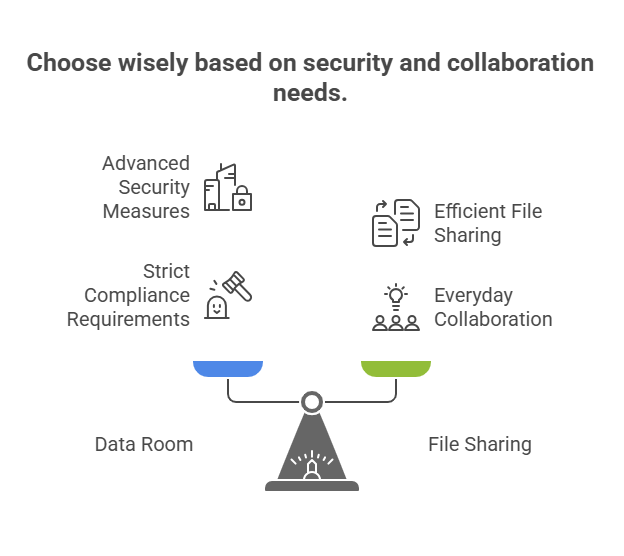
Use a data room if:
- You’re involved in M&A transactions, fundraising, or legal processes and need to share financial and legal documents with multiple stakeholders securely.
- Your industry has strict compliance requirements (finance, healthcare, legal) and must follow data privacy regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- You handle highly confidential documents, such as trade secrets, intellectual property, or financial reports.
- You need advanced security measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, watermarking, and detailed access permissions.
Use a file-sharing solution if:
- You need efficient file sharing for everyday collaboration, like marketing materials, presentations, or team projects.
- You work with non-sensitive documents that don’t require additional security measures.
- Your organization doesn’t have regulatory requirements for data storage options or compliance-heavy documentation.
Unlike general cloud storage services, VDRs provide the security and control needed for handling sensitive business transactions. If your documents require strict protection and compliance, a data room is the best choice. Otherwise, for simple collaboration, standard file-sharing tools may be sufficient.
Security risks of using file sharing for sensitive documents
One of the biggest risks of file sharing is unauthorized access to confidential data. If files are not properly secured, hackers or even employees without permission can gain access, leading to data leaks or financial loss.
For example, in 2019, a hacker, who was a former Amazon Web Services (AWS) employee, found a security flaw in Capital One’s cloud storage. This flaw allowed the hacker to access sensitive data, including credit card applications, transaction details, and customer records. Over 106 million customers were affected by the breach.
Another risk is malware and phishing attacks. In 2020, the phishing attack targeting the World Health Organization (WHO) became a major global security concern. Cybercriminals sent phishing emails that appeared to be from the WHO, asking people to click on links that would download malware. This malware could steal personal and financial information.
To strengthen data protection, organizations should use encrypted connections, multi-factor authentication, and strict access controls. These steps help protect data from cyber threats while ensuring secure file sharing.
How to transition from file sharing to a virtual data room
Switching from traditional file sharing to a virtual data room software can improve security, file access, and data management. Follow these steps for a smooth transition:
- Assess your current system. Identify how files are currently stored and shared. Check for security gaps and inefficiencies. Determine what features your business needs in a VDR.
- Choose a virtual data room provider. Compare VDR providers based on security, ease of use, and pricing. Look for essential features like user permissions, encryption, and audit logs. Consider customer support and integration with existing tools.
- Plan the migration. Set a timeline for migration to avoid disruption. Assign team roles for managing the transition. Communicate the change to all stakeholders.
- Organize and prepare your files. Clean up old and redundant files. Create an organized folder structure to ensure easy navigation.
- Set up security measures. Configure user permissions to control file access. Ensure only authorized users can view, edit, or download sensitive data.
- Upload data to the VDR. Begin with the most critical documents. Use bulk upload features to save time. Apply user permissions based on roles and access levels.
- Train employees. Provide hands-on training sessions to ensure a smooth adoption of the VDR software. Create an internal guide or FAQ to address common questions.
- Monitor and optimize. Regularly review access logs for security. Keep files updated and well-organized. Adjust permissions and settings as needed.
Key takeaways
- A virtual data room (VDR) is a secure online platform that allows businesses to access files and share documents simultaneously with multiple users, ensuring smooth collaboration.
- File-sharing solutions like Google Drive and Dropbox are convenient for everyday collaboration but lack the security features needed for confidential data.
- VDRs are commonly used in industries such as finance, legal, healthcare, and real estate, where secure data access is critical.
- Key differences between VDRs and file-sharing tools include security, user permissions, audit trails, compliance features, and scalability.
- Businesses should choose a VDR over file-sharing solutions when dealing with mergers and acquisitions, legal processes, or confidential financial transactions.
- File-sharing tools work well for non-sensitive data, marketing materials, and general collaboration but may expose businesses to security risks.
- Unauthorized access, data breaches, and phishing attacks are common risks of using basic file-sharing solutions for sensitive documents.